Hey fitness nerds!
Thank you all {{active_subscriber_count}} of you!
Despite being essential for over 300 biochemical processes in your body, magnesium remains the most chronically deficient mineral in the modern diet.
This critical nutrient could be the missing link in your health and performance goals.
Read 🔽 below!
✨
IN LESS THAN 10 MINUTES WE WILL COVER:
Weekly Insights:
Why Is Magnesium The Number 1 Mineral?
Article Explained Simple: Scientific Method to Increased Mobility
Top 3 Unconventional Signs of Dehydration
Homemade High Protein Coconut Mango Cake Pot Recipe
Looking for unbiased, fact-based news? Join 1440 today.
Join over 4 million Americans who start their day with 1440 – your daily digest for unbiased, fact-centric news. From politics to sports, we cover it all by analyzing over 100 sources. Our concise, 5-minute read lands in your inbox each morning at no cost. Experience news without the noise; let 1440 help you make up your own mind. Sign up now and invite your friends and family to be part of the informed.
Why Is Magnesium The Number 1 Mineral?

Magnesium stands as the unsung hero of minerals in human health. While calcium, iron, and zinc often receive more attention, magnesium quietly orchestrates hundreds of critical functions throughout your body.
Yet an estimated 50-75% of Americans fail to meet the recommended daily intake, creating a silent epidemic of suboptimal health and performance.
This deficiency stems from several modern factors. Agricultural practices have depleted soil magnesium content by up to 40% compared to pre-industrial levels. Food processing further strips away this mineral, with refined grains containing only 16% of the magnesium found in their whole counterparts.
Even lifestyle factors like chronic stress, regular alcohol consumption, and certain medications actively deplete the body's magnesium stores.
The consequences of insufficient magnesium are far-reaching. At the cellular level, magnesium is required for ATP production (your body's primary energy currency). Without adequate magnesium, energy production becomes inefficient, leading to unexplained fatigue that persists despite adequate sleep.
Magnesium also regulates calcium flow into muscle cells, explaining why deficiency often manifests as muscle cramps, spasms, and persistent tension.
For fitness enthusiasts, magnesium's role becomes even more critical. Exercise increases magnesium requirements by 10-20% through sweat loss and enhanced metabolic demands.
Research shows that magnesium supplementation can improve performance metrics, with one study demonstrating a 17% increase in strength among deficient athletes who corrected their levels.
Recovery is similarly enhanced, with adequate magnesium reducing post-exercise inflammation markers by up to 32%.
Sleep quality, perhaps the most underrated aspect of health optimization, depends heavily on magnesium. This mineral regulates both GABA production (a calming neurotransmitter) and melatonin synthesis. Multiple studies show magnesium supplementation improves sleep onset, duration, and efficiency—particularly in those with suboptimal levels.
Neurologically, magnesium functions as a natural NMDA receptor antagonist, essentially acting as a mild, natural anti-anxiety compound. This explains its effectiveness for stress management, with research demonstrating that restoring optimal levels can reduce cortisol production by up to 24%.
Cardiovascular health may be magnesium's most critical domain. Each heartbeat depends on precise magnesium-regulated ion channels. Deficiency has been linked to arrhythmias, hypertension, and increased cardiovascular disease risk.
One meta-analysis found that each 100mg increase in daily magnesium intake was associated with an 8% reduction in stroke risk and a 10% reduction in heart failure risk.
Metabolically, magnesium plays a central role in insulin signaling and glucose management. Low levels correlate with increased insulin resistance, with some research suggesting magnesium supplementation can improve insulin sensitivity by up to 38% in deficient individuals.
The form of magnesium matters significantly. Magnesium oxide, the most common and least expensive form, has bioavailability of only 4%, explaining why many people experience limited benefits.
Superior forms include magnesium glycinate (highly absorbable and gentle on the digestive system), magnesium malate (particularly beneficial for energy production and fibromyalgia symptoms), and magnesium threonate (the only form proven to cross the blood-brain barrier effectively, making it ideal for cognitive benefits).
Dosage considerations depend on your diet and health status. The RDA ranges from 310-420mg daily, but active individuals may benefit from up to 600mg daily from all sources.
Timing also matters, magnesium glycinate taken 30-60 minutes before bed can enhance sleep quality, while magnesium malate may provide more energy benefit when taken earlier in the day.
While supplementation offers a targeted approach, emphasizing magnesium-rich foods provides additional synergistic nutrients. Dark leafy greens, nuts (especially almonds and cashews), seeds (particularly pumpkin seeds), legumes, and dark chocolate are excellent natural sources. Interestingly, mineral water with high magnesium content (over 50mg/L) can also contribute significantly to daily intake.
The ultimate test of magnesium status isn't blood levels, as the body tightly controls serum magnesium at the expense of tissue stores but rather symptom resolution. If problems like muscle cramps, sleep disturbances, stress sensitivity, or energy fluctuations improve with supplementation, this suggests you were indeed deficient.
For a mineral that costs pennies per day to supplement, magnesium offers perhaps the highest return on investment for overall health.
Whether your goals centre on performance, recovery, stress management, or longevity, optimizing this fundamental mineral provides a foundation upon which all other health practices can build.
Hands down, the best tool for fitness, sleep, and overall wellness. 1 Month for FREE to try it out, together with a free band.


Fitness and health enthusiasts - We have a lot of things in store for you!
Check out busybody.io - and join the waitlist for our brand-new AI health app.
Article of the Week
Article Explained Simple: Scientific Method to Increased Mobility
Results showed that progressive joint distraction; a technique involving gentle traction combined with specific movement patterns, improved mobility 47% more effectively than static stretching alone.
This technique works by temporarily reducing the nervous system's protective tension response while simultaneously retraining movement patterns.
Another significant finding was that mobility improved most when participants performed shorter (5-10 minute) sessions multiple times daily rather than longer, less frequent sessions. The researchers theorized this approach better adapts the nervous system by providing frequent "reminders" about new movement capabilities.
Temperature also played a key role, performing mobility work after raising tissue temperature through light cardiovascular activity or warm showers increased effectiveness by 28%. This warmth temporarily increases tissue elasticity and reduces protective neuromuscular tension.
The researchers concluded that mobility limitations are more often neurological (the brain limiting movement to protect joints) than structural, and therefore respond best to techniques that address this protective mechanism rather than attempting to physically force tissues to lengthen.
Fascinating Fact:
Your nervous system can restrict mobility by up to 40% beyond your actual physical limitations as a protective mechanism—this "neurological reserve" explains why mobility can sometimes improve dramatically in just one session with the right techniques.
We have also started a referral program where you can earn prizes for referring your friends to this newsletter.
What other topics do you want me to write about?
Top 3 Unconventional Signs of Dehydration
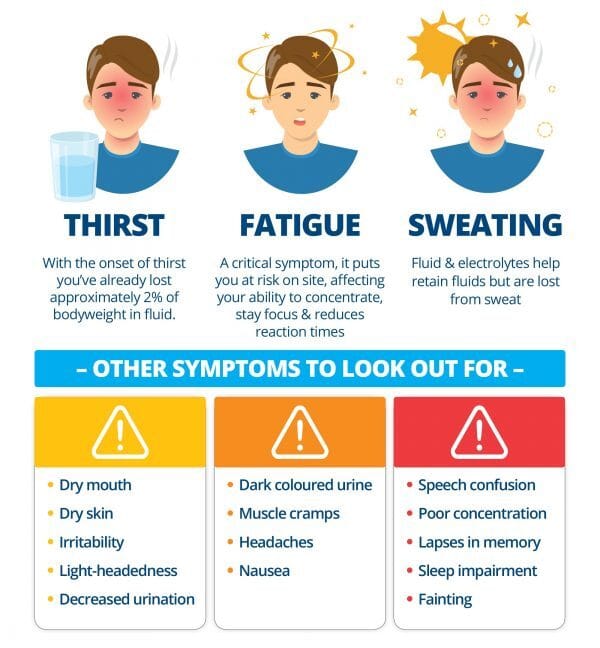
Dark Urine Color Isn't Always Reliable
While most people know to check urine colour, this indicator can be misleading. Certain supplements (especially B vitamins), foods (beets, blackberries), and medications can darken urine regardless of hydration status.More reliable is reduced urination frequency. If you haven't urinated for 4+ hours while awake, you're likely dehydrated regardless of colour. Morning urine after sleep doesn't count in this assessment since concentrated morning urine is normal.
Research shows urination frequency decreases linearly with dehydration levels, making this a more objective measure than colour alone.
Decreased Cognitive Performance
Studies show even mild dehydration (1-2% of body weight) impairs cognitive function before thirst becomes noticeable. This manifests as difficulty focusing, mathematical errors, and slower reaction times.A Stanford University study found that dehydrated participants made 12% more errors in attention-based tasks and took 23% longer to complete cognitive tests compared to when properly hydrated.
If you find yourself unusually distracted, forgetful, or making simple mistakes, try drinking 500ml of water and reassessing in 20 minutes.
Sudden Food Cravings
The body often confuses thirst and hunger signals since they originate in the same brain region (hypothalamus). Sudden, intense cravings (particularly for salty foods) frequently indicate dehydration rather than actual hunger.This confusion explains why drinking water before meals reduces calorie intake by 13% on average. If you experience sudden hunger shortly after eating, try drinking water first and waiting 15 minutes before deciding if you're actually hungry.
This mechanism becomes particularly unreliable in adults over 40, as thirst sensitivity naturally decreases with age, making this group more vulnerable to mistaking dehydration for hunger.
Vote below to choose the diet for next week’s recipe
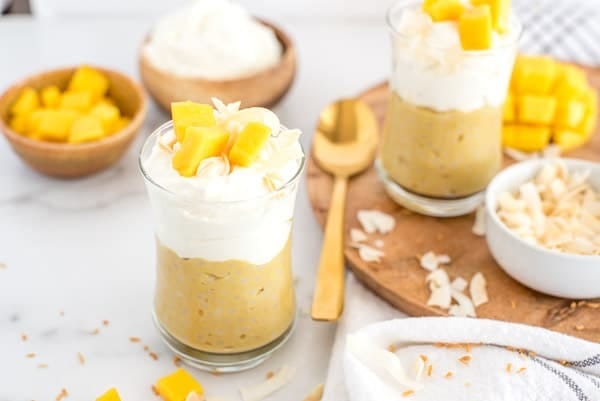
Homemade High Protein Coconut Mango Cake Pot Recipe (makes 4 servings)
This tropical-inspired dessert delivers authentic flavour with significantly improved macros compared to traditional versions.
The combination of coconut and mango provides antioxidants and healthy fats while the protein boost helps regulate blood sugar response.
This recipe was created in 2 minutes with the BusyBody App. Click the button for free access to the app.

Macros per serving
Total Calories: 225 kcal
Protein: 15 g
Carbohydrates: 22 g
Sugars: 14 g
Fat: 9 g
The Ingredients
For the cake base:
60g coconut flour (1/2 cup)
30g vanilla protein powder (1 scoop)
3 large eggs
120ml unsweetened coconut milk (1/2 cup)
2 tablespoons coconut oil, melted
2 tablespoons honey or maple syrup
1/2 teaspoon baking powder
1/4 teaspoon salt
1 teaspoon vanilla extract
For the topping:
200g Greek yoghurt (3/4 cup)
30g vanilla protein powder (1 scoop)
1 tablespoon honey or maple syrup
200g fresh mango, diced (about 1 large mango)
2 tablespoons unsweetened coconut flakes, toasted
Fresh mint leaves for garnish (optional)
The Instructions
Preheat your oven to 350°F (175°C). Lightly grease four 6-ounce ramekins or oven-safe glass jars.
In a large bowl, whisk together coconut flour, protein powder, baking powder, and salt.
In a separate bowl, beat eggs. Add coconut milk, melted coconut oil, honey or maple syrup, and vanilla extract. Mix well.
Combine wet and dry ingredients, stirring until smooth. The batter will be thick but should still be pourable. If it's too thick, add 1-2 tablespoons of water.
Divide the batter evenly among the prepared ramekins, filling each about halfway.
Bake for 15-18 minutes until the cakes are set and a toothpick inserted comes out clean. Allow to cool completely.
While the cakes are cooling, prepare the topping. Mix Greek yoghurt with protein powder and honey or maple syrup until smooth.
To assemble, spread the protein yoghurt mixture over each cooled cake. Top with diced mango and sprinkle with toasted coconut flakes.
Garnish with fresh mint leaves if desired. Serve immediately or refrigerate for up to 3 days.
For a make-ahead option, store the cakes and topping separately, assembling just before serving for the best texture.
Make your dream of working online a reality and start a newsletter - join beehiiv for free and don’t pay any renewal until you grow your subscriber base >2500 subscribers.
I’ve personally tried plenty of other platforms and Beehiiv is hands down the best and easiest to use.



